Workshops
WORKSHOP 1 – The IEEE P2784 standardization process workshop: The collaborative effort to develop a Guide for the Technology and Process Framework for Planning a Smart City
The IEEE P2784 Standardization Process Workshop is based upon the IEEE P2784 Standard Project, currently under development. This workshop is intended to provide a consistent discussion about the subject of this standard, and to identify the opinions, perception and level of knowledge of the participants about Smart Cities. For that, the organizers will base the workshop planning and dynamics on the Delphi Method and also will use dynamic interactive evaluation tools, such as Google Forms and Mentimeter. The objective is not only to present the content and current status of the standardization process to the attendees, but also to collect some suggestions from them. The idea of this workshop is to have a very interactive, participative, and democratic discussion about the content and scope of this Standard Project. The expected outcome is to develop a study based on the insights of the participants as well as the surveys and polling collected before, during, and after the workshop.
After the event, all attendees will receive some handouts, including a study guide for the IEEE P2784 standard and the summary of the survey results from this interactive workshop. This workshop is an opportunity forthe attendees of the IEEE ISC2 conference to learn what is involved in the development of a standard that aims to help cities to plan, implement and operate Smart Cities Solutions. This is challenging because it needs to accommodate not only the technology trends and applications in the cities, but also the implications of their deployment as well as the multiple stakeholders involved in this process. From the normative perspective, the standard is required to be aligned with the best practices, comprehending the multiple dimensions involved in the contemporary cities.
+ More Infos
The main targeted audience are academic and practitioners in the Smart Cities area of expertise; public works personnel, consulting engineers, utility staff, resilience and sustainability experts, planners, community leaders. The general public are also strongly encouraged to attend, in order to bring the citizen perspective.
ORGANIZERS

Larissa Paredes Muse
Vice-Chair of the IEEE Smart City Planning and Technology Guide Standard P2784 Associated research fellow at Brazilian Network for Smart & Human Cities – RBCIH | Atlanta-Brazil relationship

Jim Frazer
Chair of the IEEE Smart City Planning and Technology Guide Standard P2784 VP Smart Cities – ARC Advisory Group | Chair Illuminating Engineering Society’s Roadway Lighting Committee

Eduard Fidler
Secretary of the IEEE Smart City Planning and Technology Guide Standard P2784 Lead Transportation Analyst – ARC Advisory Group
PRELIMINARY PROGRAM
1 – Invited Talks
Presenter: Larissa Paredes Muse, IEEE Smart Cities Community
Abstract: The contemporary cities face innumerous problems resultant from the inequity of public polices and the lack of responsible long-term planning. At the same time, the cities witness the digital transformation and the rise and pervasiveness of ICTs. This presentation aims to provide a contextualized overview of the main Smart City drivers, as well as the main barriers and benefits involved in the process of planning, deploy and operate Smart City solutions and technologies.
Presenter: Jim Frazer, ARC Advisory Group
Abstract: In this presentation, five broad groups of human factors are discussed. They include social, technological, economic, environmental and political groups. Within each of these grouping twenty factors each will be introduced. Additionally, the impact of these factors on sustainability, resilience and the digital transformation of the city ecosystem will be examined.
Presenter: Eduard Fidler, ARC Advisory Group
Abstract: The previous two presentations in the workshop address what is driving and inhibiting, as well as the various human factors involved within the development of smart cities. This presentation will introduce and briefly explore the nine vertical applications and seven enabling technologies relevant to smart city planning, establishing a common point of reference for a subsequent discussion of attendee priorities and challenges around each. The verticals consist of the built environment, energy infrastructure, telecommunications systems, transportation, health & human services, water & wastewater, waste management, public safety, and payments & finance. The enabling technologies consist of instrumentation & control, connectivity, interoperability, security & privacy, data management, computing resources, and analytics.
Presenter: Jim Frazer, ARC Advisory Group
Abstract: The author introduces the waterfall model as well as an agile scrum approach to smart city planning, deployment, management, operations and eventual decommissioning / retirement of the system. Include in the presentation is specific guidance on:
• How to identify stakeholder communities;
• How to document needs of the communities, and how to build a list of consensus-based needs;
• How to refine consensus-based needs into measurable functional requirements;
• How to develop a request for information (RFI) and request for proposal (RFP);
• How to develop and implement test plans to keep you on track;
• How to manage smart city projects over their entire lifecycle;
2 – Discussion Panels
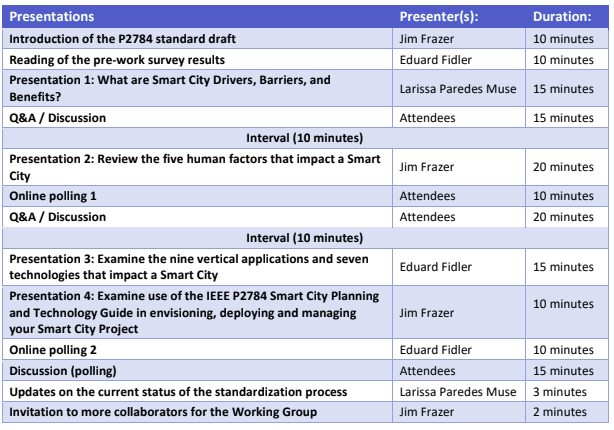
Some discussions in between the presentations and hands-on activities are planned to engage the attendees (Please see the table of the Workshop Dynamics).
WORKSHOP 2 – The 3rd International Workshop on BLockchain Enabled Sustainable Smart Cities (BLESS 2020)
Enabled by the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), edge-fog-cloud computing, and interconnected networks, smart cities are capable of innovative solutions to change the lifestyles of its residents. Unavoidably the potential benefits come along with new challenges and concerns related to information security and privacy. Blockchain technology is a platform that would provide tamper-proof storage for data derived from smart cities and ensure the access to the data is tracked and provided to authorized users. The resultant chain of custody will provide an interoperable platform that would facilitate decisions in smart cities that would impact the communities. The transparency of the platform would provide citizens would go a long way in building trust and ensure that the businesses will held to high standards of accountability.
Specifically, BLESS’2020 highlights the roles that blockchain technology plays in the smart cities, it is cross-disciplinary and covers multiple area including information security, infrastructure security, facilities, communication networks, data storage, distributed computing, and more. This workshop gathers researchers from these areas together to foster the collaboration among such interdisciplinary areas and to spark discussion on open topics related to blockchain enabled applications in smart cities.
The audience is expected to come from multiple areas including information security, infrastructure security, facilities, communication networks, data storage, distributed computing, etc.
ORGANIZERS

Yu Chen

Sachin Shetty
PRELIMINARY PROGRAM
This year, BLESS 2020 workshop consists of an oral presentation session with four talks.
Presenter: Dr. Chin-Tser Huang, University of South Carolina, USA
Abstract: Counterfeit electronic parts have posed a serious threat to consumers, industry, and government and military agencies for a long time. They not only lead to massive damage in terms of financial and reputation losses, but can also create high risk in the compromise of system safety and integrity. Our previous work shows the possibility of achieving the decentralized runtime verification by incorporating some mechanisms of the blockchain technology into a distributed system for locating the accountability when error occurs. In this paper, we propose to develop a verification framework based on blockchain technology to detect the abnormalities of counterfeit ICs at every stage of their lifecycles, including after being deployed into the system. We design an efficient and effective method that can store the inspection and testing results into a blockchain, and apply the smart marker scheme which can merge separate blockchains associated with individual ICs into one blockchain after the ICs are installed onto the same system.
Presenter: Dr. Sachin Shetty, Old Dominion University, USA
Abstract: Smart cities deal with connected things which produce large amounts of data. Their applications need to support high scalability, high transaction throughput, high backend load, and data analytics features. The data accumulated in smart cities are highly critical since it can be used to improve the operations across the cities. To guarantee the security and privacy of the data generated in smart city applications, blockchain-based decentralized infrastructure can be adopted. However when integrating existing blockchain systems with smart city applications, one encounters many challenges. Current blockchains do not support high transaction throughput; it does not provide high scalability; it does not provide realtime transaction processing; it does not provide full-text search query APIs; it does not handle back-end stress operations and so on. As a result, it is hard to incorporate existing blockchain systems for smart city applications. In this paper, we propose a highly scalable blockchain platform, “Bassa”, for smart city applications, which supports real-time transaction enabled “validate-execute-group” blockchain architecture to increase the transaction throughput of the blockchain. It comes with a functional programming and actor-based smart contract platform that enables concurrent execution of transactions in the blockchain. Bassa supports high transaction throughput, high scalability, concurrent transaction execution, data analytics and machine learning features on the blockchain. With Bassa, we provide a blockchain platform that can provide acceptable performance on the highly scalable applications (e.g Smart Cities).
Presenter: Mr. Ronghua Xu, Binghamton University, USA
Abstract: Advancement in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Big Data technologies is reshaping the global economy. The community currency network is receiving more attention through enhancing social ties within a community. As the most popular type of community currency, Time Banking (TB) is a generalized community exchange economy, which uses the time to evaluate participant’s contributions on the same scale rather than any equivalence with the official national currency. TB is a noble idea with the potential to improve the quality of life through reciprocally beneficial activities among community members. However, it also brings new concerns about security and trust issues. Inspired by blockchain and smart contract, this paper introduces a Blockchain Integrated Time Banking System (BIT) to secure a decentralized community exchange economy. In BIT system, the service providers and recipients can securely commit service exchange through the self-executing smart contract without relying on a third-party trust authority. Blockchain network ensures immutability, auditability, and traceability of all data and service transactions recorded on the distributed ledger. A proof-of-concept prototype is implemented and tested on a private Ethereum network. The experimental results verify the feasibility of the proposed BIT, which provides decentralized community service exchanges with limited computation overhead and network latency.
Presenter: Mr. Mimal Ghimire, Howard University, USA
Abstract: Many research problems are not solved because of the need for enormous computation complexity and time complexity. Crowd sourcing approach has been applied to bring people and resources together to accomplish complex tasks collaboratively. This research studies an alternate and viable approach for solving computationally intensive tasks. Public blockchain technology has demonstrated gigantic computing potential by the participation of computing machines around the world. In this talk, we propose an approach that utilizes the power of blockchain technology to find solutions or improvement to the existing solutions of NP-complete problems. Furthermore, out study focuses on how blockchain can be utilized to verify any given solutions. Specifically, in this work, we propose a smart contract based approach to deploy NP-complete problems in the blockchain network. The blockchain is utilized to compute the proposed solution given by anyone connected in the network. If any proposed solution or improvement on the existing solution meets specified criteria, it is permanently stored in the blockchain. For a valid solution, the solver gets the reward for providing a valid solution that could be used by many other participating units.
WORKSHOP DYNAMICS
The BLESS 2020 workshop will be done in an oral presentation session of two hours (120 minutes) as follows:
| Presentations | Presenter | Duration |
| Welcome & Opening Remarks | Dr. Sachin Shetty | 10 minutes |
| Detecting Counterfeit ICs with Blockchain-based Verification Framework | Dr. Chin-Tser Huang | 25 minutes |
| Bassa - Scalable Blockchain Architecture for Smart Cities | Dr. Sachin Shetty | 25 minutes |
| BIT: A Blockchain Integrated Time Banking System for Community Exchange Economy | Mr. Ronghua Xu | 25 minutes |
| Toward Smart Contract for Solving NP-Complete Problems in Emerging Smart Applications | Mr. Bimal Ghimire | 25 minutes |
| Closing Remarks | Dr. Yu Chen | 10 minutes |
OUTCOMES
BLESS’2020 aims at bringing researchers and experts together to present and discuss the latest developments and technical solutions concerning various aspects of blockchain technology in the context of smart cities. The presentations and discussions will inspire new thoughts and ideas, and potential collaborations.